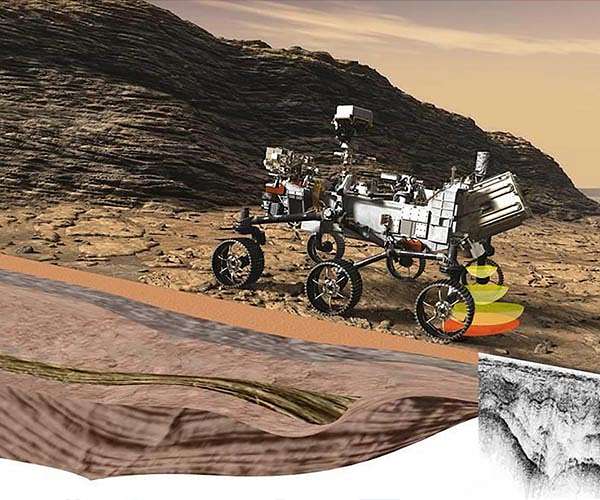
Searching for buried treasure on Mars with RIMFAX (Image Credit: Space Daily)
What do the Perseverance rover and Superman have in common? They both can “see” through solid rock! Superman has X-ray vision whereas Perseverance has RIMFAX, a ground penetrating radar or GPR, located on the lower rear of the rover. RIMFAX uses radio waves to image the subsurface rock layers as the rover drives along.
It is the first instrument of its kind sent by NASA to Mars and can “see” down to 10 meters (33 feet) depth. As the rover drives along, RIMFAX sends out a radio signal into the surface. When the radio waves encounter a new rock layer, some waves bounce back up toward RIMFAX. RIMFAX detects these return signals and stacks them up, building an image of the subsurface rock layers.
The speed the waves travel through rock depends on the rock’s properties, summarized by a quantity called permittivity. Different rock types have known permittivity values; therefore, scientists can constrain the rock type of each layer. The tilt of the layers also indicates the conditions they were deposited in.
Figuring out the order different layers of rocks were deposited in allows scientists to tease out the climate history of the area and could tell us if liquid water once existed there and for how long. The first results returned by RIMFAX from the crater floor show that GPR works great on Mars, even compared to most places on Earth! This is because it’s so cold on Mars that there’s no liquid water below the surface, which limits the penetration of radar waves on Earth.
The results showed that the rock layers have a high permittivity value, corresponding to igneous rocks, whereas the tilt of the rock layers indicate they could have been deposited by a long period of volcanic activity or when the crater was covered with liquid water.
Determining which of these processes formed the subsurface layers can be aided by collecting more data as Perserverance drives along, and by observations from the other instruments on the rover. Since leaving the crater floor, RIMFAX has also detected sedimentary rocks as well as igneous. This information will provide useful context for scientists back on Earth when they analyze the rover’s samples.
Related Links
Perseverance Mars 2020
Mars News and Information at MarsDaily.com
Lunar Dreams and more
|
|
Tweet |
|
|
|
We need your help. The SpaceDaily news network continues to grow but revenues have never been harder to maintain. With the rise of Ad Blockers, and Facebook – our traditional revenue sources via quality network advertising continues to decline. And unlike so many other news sites, we don’t have a paywall – with those annoying usernames and passwords. Our news coverage takes time and effort to publish 365 days a year. If you find our news sites informative and useful then please consider becoming a regular supporter or for now make a one off contribution. |
||
|
SpaceDaily Contributor $5 Billed Once credit card or paypal |
SpaceDaily Monthly Supporter $5 Billed Monthly paypal only |
|
NASA launches Mars Sample Receiving Project Office at Johnson
Houston TX (SPX) Jan 25, 2023
NASA announced Thursday its new Mars Sample Receiving Project office, responsible for receiving and curating the first samples returned from the Red Planet, will be located at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. The safe and rapid release of Mars samples after they return to Earth to laboratories worldwide for science investigations will be a priority.
The office will reside within Johnson’s Astromaterials Research and Exploration Science division, NASA’s organization with expertise in p … read more









