Scientists finally found 2 of the Milky Way’s missing satellite galaxies. What could this mean for astronomy? (Image Credit: Space.com)
Astronomers have discovered two new satellite galaxies of the Milky Way, and these findings could help us better understand dark matter — the mysterious stuff that accounts for around 85% of the matter in the universe yet remains effectively invisible to us.
The discoveries also move scientists a step closer to solving a lingering problem with the standard model of cosmology, or the “lambda cold matter model,” also known as “ΛCDM,” in which the word “cold” assumes dark matter is composed of particles moving slower than the speed of light.
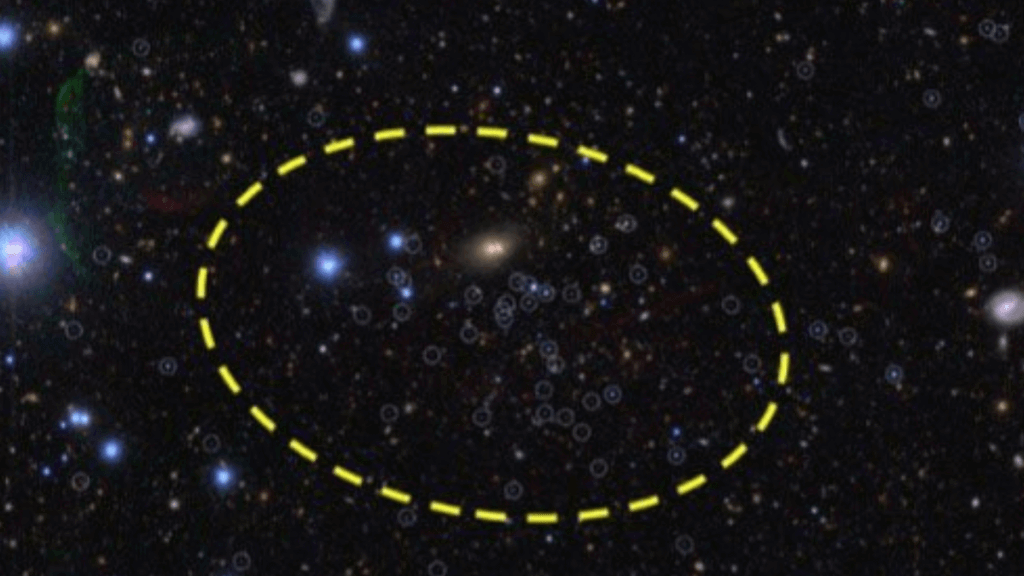
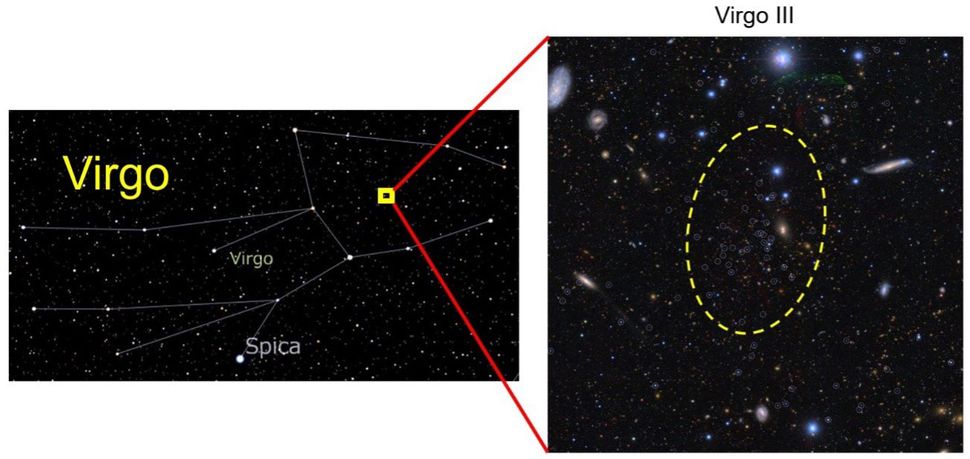
The newly found small gatherings of stars have been designated Sextans II and Virgo III. They join the around 60 known dwarf galaxies that swarm around our much larger home spiral galaxy at maximum distances of 1.4 million light-years. The most famous and largest of these dwarf galaxy satellites of the Milky Way are the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) and the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC).
“How many satellite galaxies does the Milky Way have? This has been an important question for astronomers for decades,” team leader Masahi Chiba, a professor at Tohoku University, said in a statement.
Related: Amateur astronomer finds 5 fascinating new galaxies — and they’re now named after him
Many tiny dwarf galaxy satellites of the Milky Way remain undiscovered due to their distant and faint nature, but Chiba and colleagues were determined to start finding these elusive objects. So, they turned to the Subaru telescope. This powerful ground telescope, located near the summit of Maunakea, Hawaii, is well-suited to hunting dwarf galaxies, and the same team had previously used it to detect three new satellites of the Milky Way.
Help! Our dwarf galaxies are missing
Dark matter is a lingering cosmological problem because it neither interacts with light nor the ordinary matter that composes stars, planets, moons and us. And, well, if it does interact with those things, those interactions are far too weak for us to notice.
That means dark matter could be composed of particles that are currently undiscovered, though there are potential explanations that don’t require extensions to particle physics. For instance, scientists have explored the idea that dark matter could be made of tiny primordial black holes left over from just after the Big Bang.
However, dark matter indeed interacts with gravity, which can influence the motion and dynamics of light and everyday matter. This has allowed scientists to infer the presence of dark matter, and eventually determine that large galaxies are surrounded by vast haloes of this mysterious substance. Those halos, it’s believed, extend far beyond galactic disks and halos of visible matter.
The ΛCDM predicts that these dark matter halos have played a significant role in the evolution of galaxies. In the early universe, they formed gravitational wells into which the gas and dust that formed stars within galaxies were drawn. Eventually, these halos also drew together, forming large galaxies like the Milky Way.

This model also suggests there should really be hundreds of satellite galaxies around the Milky Way and other major galaxies. For instance, simulations using ΛCDM predict that our neighboring galaxy, Andromeda, should be surrounded by around 500 satellite galaxies. Yet, astronomers have seen just 39 dwarf galaxies swirling around Andromeda.
For the Milky Way, some simulations based upon the standard model of cosmology indicate that our galaxy should be orbited by about 220 dwarf galaxies, yet scientists can’t figure out where they all are. The discovery of Sextans II and Virgo III helps to redress that balance. Still, results spinning out of these findings could present cosmologists with the opposite problem they were facing before this.

Not enough dwarf galaxies or too many?
Though the number of Milky Way galaxies identified is still well below the predicted 220 dwarf galaxies, the team behind this research took into account the fact that the Subaru can’t see the entirety of the night sky over Earth.
They combined the distribution of dwarf galaxies Subaru has been able to see with its night-sky “footprint” to calculate an estimate for how many satellites should, in reality, surround our galaxy. This led to the calculation that 500 galaxies surround the Milky Way — over double the amount predicted by simulations based on the ΛCDM.
So, have scientists gone from a “not enough dwarf galaxies problem” to a “too many dwarf galaxies” problem?

Maybe not. Recently, amateur astronomer Giuseppe Donatiello discovered five new satellite galaxies around the Sculptor galaxy, officially known as NGC 253.
When he and a team of astronomers looked at the distribution of satellite galaxies around the sculptor galaxy, including three previously found by Donatiello himself, they found that the distribution of these galaxies, which sit around 11.5 million light-years away from Earth, was uneven. In other words, the tiny galaxies seemed to have a “favored direction,” with more galaxies lying to one side of the Sculptor galaxy than the other.
If there is also a favored direction to dwarf galaxies around the Milky Way and the Suburu telescope happened to be looking this way, then the estimates based on Subaru’s observations would be inflated.
The team behind these Milky Way dwarf galaxy findings now intends to further investigate the actual number of satellite galaxies surrounding us with yet another ground telescope.
“The next step is to use a more powerful telescope that captures a wider view of the sky,” Chiba concluded. “Next year, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile will be used to fulfill that purpose. I hope that many new satellite galaxies will be discovered.”
The team’s results were published on June 8 in the Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan.





