by Erika Peters
NASA’s Johnson Space Center
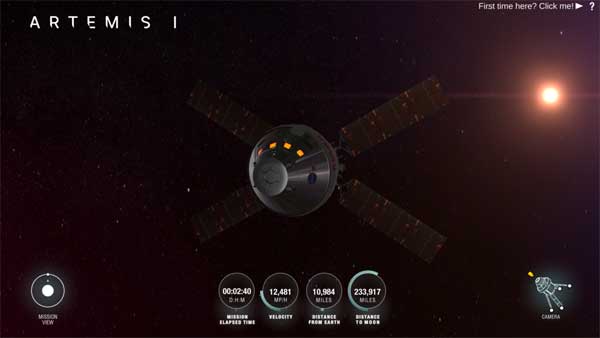
HOUSTON — Join NASA’s Orion spacecraft on its first mission around the Moon using the Artemis Real-time Orbit Website (AROW) to track the spacecraft’s flight as it happens.
On the web, users can follow AROW to see where Orion is in relation to the Earth and the Moon and follow Orion’s path during the mission.
During Artemis I, Orion will travel to 40,000 miles beyond the Moon in the first integrated flight test with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Using AROW, almost anyone with internet access can pinpoint where Orion is and track its distance from the Earth, distance from the Moon, mission duration, and more. AROW will be available beginning Aug. 28 on NASA’s website and on the @NASA_Orion Twitter account.
AROW visualizes data collected by sensors on Orion and sent to the Mission Control Center at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston during its flight. It will provide periodic real-time data beginning about one minute after liftoff through separation of the SLS rocket’s Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage approximately two hours into flight. Once Orion is flying on its own, AROW will provide constant real-time information.
“This is a really powerful way to engage with the mission and understand the scope of what NASA is trying to accomplish with Artemis I,” said Seth Lambert, the Orion programmer who created AROW.
On the web, users can follow AROW to see where Orion is in relation to the Earth and the Moon and follow Orion’s path during the mission. Users can view key mission milestones, and characteristics on the Moon, including information about landing sites from the Apollo program. Also available for download will be trajectory data from the flight, called an ephemeris.
Follow Orion’s Twitter account for mission milestone updates shared by AROW, including Orion’s velocity, temperature, distance, and mission elapsed time.
Follow Orion’s Twitter account for mission milestone updates shared by AROW, including Orion’s velocity, temperature, distance, and mission elapsed time.
AROW also will provide a set of Orion’s state vectors — data that describes precisely where Orion is located in space and how it moves — for inclusion in these tweets once Orion is flying on its own. These vectors can be used for data lovers, artists, and creatives to make their own tracking app, data visualization, or anything else they envision.
“Knowing what the spacecraft is doing during the mission is already cool, but now that Orion’s data can be visualized in all these different ways, it will be interesting to see what creative projects others come up with,” said Richard Garodnick, an engineer on the mission control center system engineering and development team at Johnson.
And while the app was developed and will be used for Artemis missions, the technology behind AROW could be applied to other missions in the future.
Through Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone to send astronauts to Mars.
Learn more about the Orion spacecraft at: