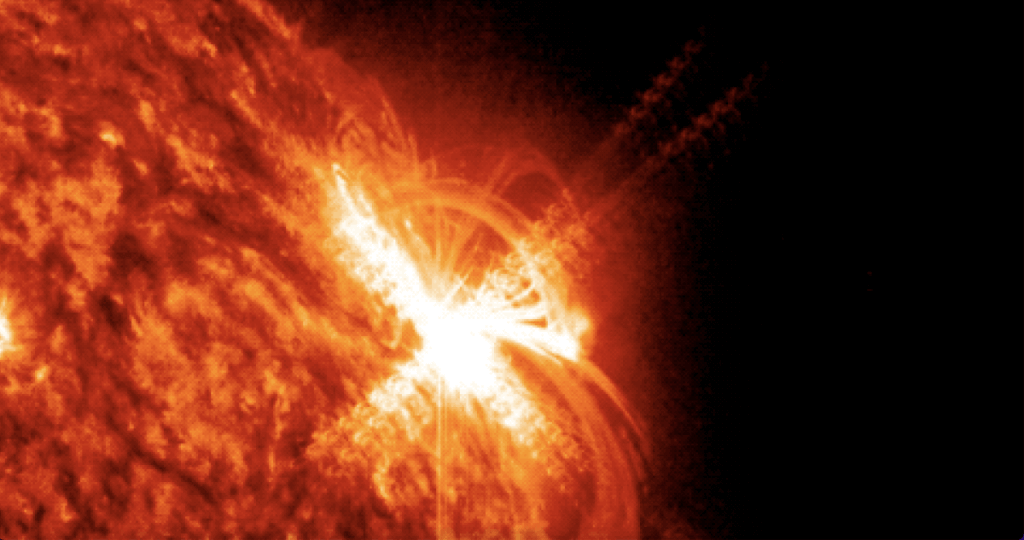
The sun blasted out a superpowerful X-class flare on Friday afternoon (March 3), and a NASA spacecraft captured footage of the dramatic event.
The solar flare — an intense burst of high-energy radiation — erupted Friday at 12:52 p.m. EST (1752 GMT). It registered as an X2.1, NASA officials said (opens in new tab), meaning it was particularly intense. (Solar scientists categorize potent flares into three categories, with C being the weakest, M being medium-strength and X the most powerful.)
The power of Friday’s flare is on full display in footage captured by NASA’s Earth-orbiting Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), which has been studying the sun in detail since 2010.
Related: The worst solar storms in history
Radiation from the flare, which erupted from a sunspot called AR 3234, caused a shortwave radio blackout over North and South America, according to SpaceWeather.com (opens in new tab).
“Aviators and ham radio operators may have noticed loss of signal and other unusual propagation effects at frequencies below 30 MHz for as much as an hour after the flare,” the outlet wrote.
Powerful flares are often accompanied by coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which send huge clouds of solar plasma rocketing into space at millions of miles per hour. These clouds can spawn geomagnetic storms here on Earth, which in turn can affect power grids and orbiting spacecraft, as well as supercharge our planet’s auroral displays.
It’s unclear at the moment if a CME did erupt in concert with Friday’s X2.1 flare, or if that CME would be headed toward Earth. (Some of these plasma clouds miss our planet.)
Friday’s flare didn’t come out of the blue: The sun has been extremely active lately, firing off a number of strong flares and CMEs.
For example, solar outbursts triggered strong geomagnetic storms in the last few days of February. These storms ramped up auroras, dazzling skywatchers around the world.
These dancing atmospheric light shows, which are usually confined to very high latitudes, were observed as far from the poles as California’s Death Valley and Perth, the capital of Western Australia.
Solar activity waxes and wanes on an 11-year cycle. Earth’s star is clearly in an active phase of the current cycle at the moment, so we should be on the lookout for more outbursts.
Mike Wall is the author of “Out There (opens in new tab)” (Grand Central Publishing, 2018; illustrated by Karl Tate), a book about the search for alien life. Follow him on Twitter @michaeldwall (opens in new tab). Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) and on Facebook (opens in new tab).