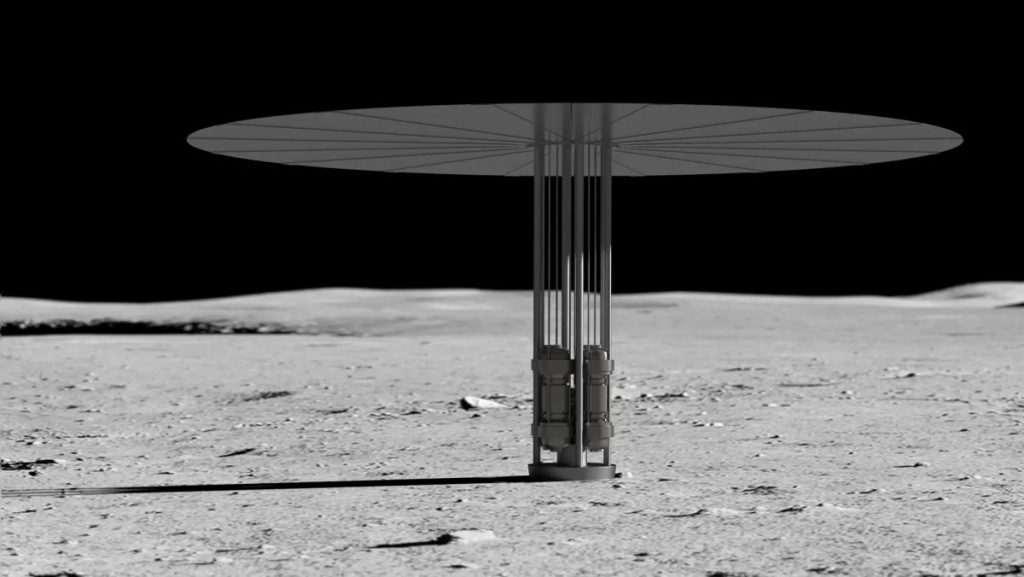
Three companies will demonstrate their potential to power lunar infrastructure using nuclear fission systems, under new joint NASA contracts announced on Tuesday (June 21).
NASA and the U.S. Department of Energy selected three design concept proposals that the government hopes could be ready for use on the moon by the end of the 2020s, to support the space agency’s Artemis program of lunar exploration.
NASA also sees these contracts, valued at $5 million each, as potentially useful for the exploration of Mars and other deeper-space destinations.
“Developing these early designs will help us lay the groundwork for powering our long-term human presence on other worlds,” Jim Reuter, associate administrator for NASA’s space technology mission directorate, said in an agency press release (opens in new tab).
Related: US military wants to demonstrate new nuclear power systems in space by 2027
The selected teams are led by Lockheed Martin, Westinghouse and IX (a joint venture of Intuitive Machines and X-Energy). Their aim in the next 12 months is to “provide NASA critical information from industry that can lead to a joint development of a full flight-certified fission power system,” the agency stated.
These are Phase 1 awards; NASA did not outline in the press release what the timeline would be for a Phase 2 contract, if that indeed is part of the plan.
The newly announced contracts are joining a quickly growing group of nuclear space initiatives, mostly on the military side, to further U.S. government work in lunar exploration and deep space in general.
On May 17, for example, the U.S. Defense Innovation Unit announced two prototype contracts for spacecraft nuclear propulsion and power, aiming to have an orbital flight demonstration in 2027.
And on May 4, the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) announced its next stage of a project to design, develop and assemble a nuclear thermal rocket engine for a flight demonstration in Earth orbit in 2026.
While the U.S. military is pursuing this work to monitor commercial and government activities in cislunar space, NASA is also thinking through nuclear opportunities for crewed exploration.
For example, NASA’s fiscal 2023 budget request, not yet approved by Congress, includes $15 million (opens in new tab) to support nuclear propulsion. The agency is also collaborating with DARPA’s Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations (DRACO) program, which aims to develop a nuclear thermal propulsion system for use in Earth-moon space.
Follow Elizabeth Howell on Twitter @howellspace (opens in new tab). Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) and on Facebook (opens in new tab).