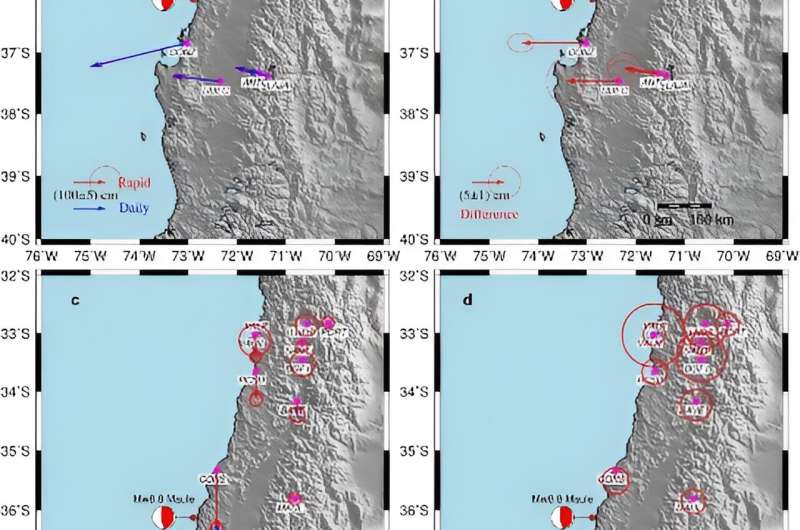
The aftermath of an earthquake is marked by intricate postseismic adjustments, particularly the elusive early afterslip. Daily seismic monitoring has struggled to capture the rapid and complex ground movements occurring in the critical hours post-quake.
The intricacies of these initial activities and their profound implications for seismic hazard assessment highlight an urgent need for more refined and immediate monitoring techniques.
In a paper published on July 29, 2024, in Satellite Navigation, Wuhan University researchers report their meticulous examination of the Maule earthquake‘s early afterslip. Using sub-daily GPS solutions, the study delivers a comprehensive narrative of the ground surface deformations occurring in the pivotal hours following the earthquake.
This study employs sub-daily GPS data to provide a high-resolution depiction of the 2010 Mw 8.8 Maule earthquake’s postseismic afterslip. The innovative approach captures the rapid ground deformations that typically elude daily GPS measurements, revealing a nearly 10% reduction in the overestimation of coseismic displacements.
The research illustrates the predominance of afterslip in the first 36 hours, overshadowing poroelastic effects, and contributes significantly to seismic hazard assessment. The findings enhance the clarity and depth of our understanding of the Earth’s postseismic dynamics, offering a robust tool for improving early warning systems and disaster response strategies.
Dr. Yangmao Wen, the study’s corresponding author said, “Our research demonstrates the sub-daily GPS’s adeptness at capturing the intricate dynamics of early afterslip, which is crucial for evaluating seismic risks and deciphering fault behavior post-earthquakes.”
The deployment of sub-daily GPS in seismic studies heralds a new era in hazard management. It enables a more accurate and expedited assessment of postseismic activities, allowing for more effective responses to earthquake impacts.
The enhanced accuracy in early afterslip measurements is set to improve aftershock predictions, optimize emergency preparedness, and mitigate the seismic vulnerability of at-risk communities. This advancement in geodetic monitoring is a step change towards a more profound comprehension of earthquake dynamics and their societal implications.
More information:
Kai Liu et al, Rapid early afterslip characteristics of the 2010 moment magnitude (Mw) 8.8 Maule earthquake determined with sub-daily GPS solutions, Satellite Navigation (2024). DOI: 10.1186/s43020-024-00145-6
Provided by
Wuhan University
Mapping the invisible: How sub-daily GPS sheds light on early postseismic deformation (2024, August 5)
retrieved 5 August 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-08-invisible-daily-gps-early-postseismic.html
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.