This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com’s Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights.
Mike Sori is an Assistant Professor of Planetary Science at Purdue University.
On Oct. 14, 2024, NASA launched a robotic spacecraft named Europa Clipper to Jupiter’s moons. Clipper will reach the ice-covered Jovian moon Europa in 2030 and spend several years collecting and sending valuable data on the moon’s potential habitability back to Earth.
Clipper isn’t the only mission highlighting researchers’ interest in Jupiter and its moons.
On April 13, 2023, the European Space Agency launched a rocket carrying a spacecraft destined for Jupiter. The Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer – or JUICE – will spend at least three years on Jupiter’s moons after it arrives in 2031.
I’m a planetary scientist who studies the structure and evolution of solid planets and moons in the solar system.
There are many reasons my colleagues and I are looking forward to getting the data that Europa Clipper and JUICE will hopefully be sending back to Earth in the 2030s. But perhaps the most exciting information will have to do with water. Three of Jupiter’s moons – Europa, Ganymede and Callisto – are home to large, underground oceans of liquid water that could support life.
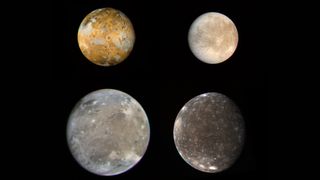
Meet Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto
Jupiter has dozens of moons. Four of them in particular are of interest to planetary scientists.
Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto are, like Earth’s Moon, relatively large, spherical complex worlds. Two previous NASA missions have sent spacecraft to orbit the Jupiter system and collected data on these moons. The Galileo mission orbited Jupiter from 1995 to 2003 and led to geological discoveries on all four large moons. The Juno mission is still orbiting Jupiter today and has provided scientists with an unprecedented view into Jupiter’s composition, structure and space environment.
These missions and other observations revealed that Io, the closest of the four to its host planet, is abuzz with geological activity, including lava lakes, volcanic eruptions and tectonically formed mountains. But it is not home to large amounts of water.
Europa, Ganymede and Callisto, in contrast, have icy landscapes. Europa’s surface is a frozen wonderland with a young but complex history, possibly including icy analogs of plate tectonics and volcanoes. Ganymede, the largest moon in the entire solar system, is bigger than Mercury and has its own magnetic field generated internally from a liquid metal core. Callisto appears somewhat inert compared to the others, but serves as a valuable time capsule of an ancient past that is no longer accessible on the youthful surfaces of Europa and Io.
Most exciting of all: Europa, Ganymede and Callisto all almost certainly possess underground oceans of liquid water.
Ocean worlds
Europa, Ganymede and Callisto have chilly surfaces that are hundreds of degrees below zero. At these temperatures, ice behaves like solid rock.
But just like Earth, the deeper underground you go on these moons, the hotter it gets. Go down far enough and you eventually reach the temperature where ice melts into water. Exactly how far down this transition occurs on each of the moons is a subject of debate that scientists hope to resolve with JUICE and Europa Clipper. While the exact depths are still uncertain, scientists are confident that these oceans exist.
The best evidence of these oceans comes from Jupiter’s magnetic field. Saltwater is electrically conductive. So as these moons travel through Jupiter’s magnetic field, they generate a secondary, smaller magnetic field that signals to researchers the presence of an underground ocean. Using this technique, planetary scientists have been able to show that the three moons contain underground oceans. And these oceans are not small – Europa’s ocean alone might have more than double the water of all of Earth’s oceans combined.
An obvious and tantalizing next question is whether these oceans can support extraterrestrial life. Liquid water is an important piece of what makes for a habitable world, but far from the only requirement for life. Life also needs energy and certain chemical compounds in addition to water to flourish. Because these oceans are hidden beneath miles of solid ice, sunlight and photosynthesis are out. But it’s possible other sources could provide the needed ingredients.
On Europa, for example, the liquid water ocean overlays a rocky interior. That rocky seafloor could provide energy and chemicals through underwater volcanoes that could make Europa’s ocean habitable. But it is also possible that Europa’s ocean is a sterile, inhospitable place – scientists need more data to answer these questions.
Upcoming missions from ESA and NASA
Europa Clipper and JUICE are set up to give scientists game-changing information about the potential habitability of Jupiter’s moons. While both missions will gather data on multiple moons, JUICE will spend time orbiting and focusing on Ganymede, and Europa Clipper will make dozens of close flybys of Europa.
Both of the spacecraft will carry a suite of scientific instruments built specifically to investigate the oceans. Onboard radar will allow Europa Clipper and JUICE to probe into the moons’ outer layers of solid ice. Radar could reveal any small pockets of liquid water in the ice, or, in the case of Europa, which has a thinner outer ice layer than Ganymede and Callisto, hopefully detect the larger ocean.
Magnetometers will also be on both missions. These tools will give scientists the opportunity to study the secondary magnetic fields produced by the interaction of conductive oceans with Jupiter’s field in great detail and will hopefully give researchers clues to salinity and volumes of the oceans.
Scientists will also observe small variations in the moons’ gravitational pulls by tracking subtle movements in both spacecrafts’ orbits, which could help determine if Europa’s seafloor has volcanoes that provide the needed energy and chemistry for the ocean to support life.
Finally, both craft will carry a host of cameras and light sensors that will provide unprecedented images of the geology and composition of the moons’ icy surfaces.
Maybe one day, a spacecraft will be able to drill through the miles of solid ice on Europa, Ganymede or Callisto and explore oceans directly. Until then, observations from spacecraft like Europa Clipper and JUICE are scientists’ best bet for learning about these ocean worlds.
When Galileo discovered these moons in 1609, they were the first objects known to directly orbit another planet. Their discovery was the final nail in the coffin of the theory that Earth – and humanity – resides at the center of the universe. Maybe these worlds have another humbling surprise in store.

