NASA’s next-generation space telescope has completed tests of another science instrument, bringing it another step closer to starting formal operations.
The $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope (JWST or Webb) — NASA’s largest and most powerful space science observatory — will search the cosmos to uncover the history of the universe’s first galaxies and the formation of stars and planets. NASA officials plan to release the first operational images from the telescope, which launched on Dec 25, 2021, on July 12 during a live event you can watch here at Space.com.
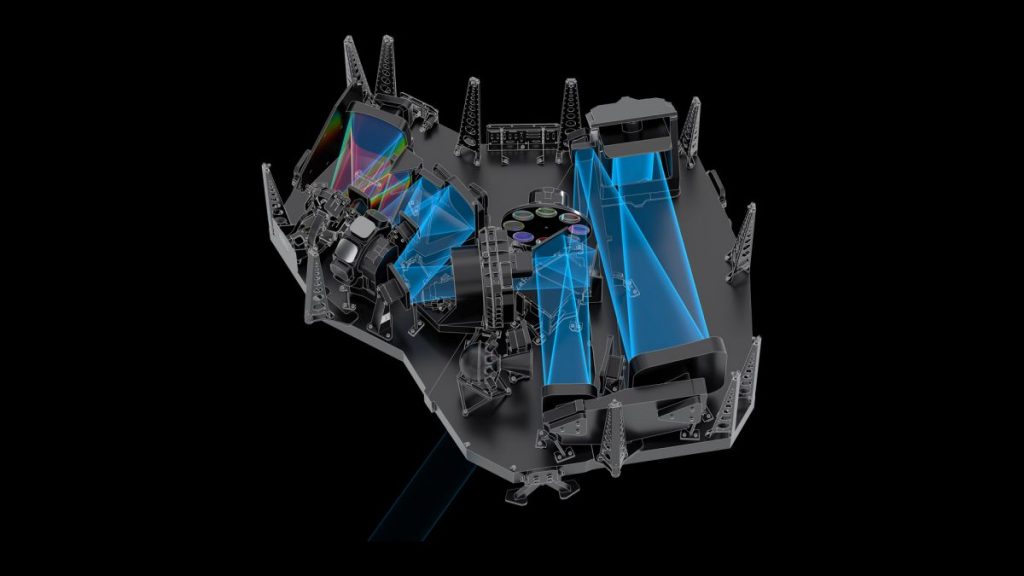
The latest instrument to be tested, calibrated and verified by the mission team was the telescope’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec). This instrument has four key modes, which the team officially confirmed are ready to begin science operations, according to a statement from NASA; NIRSpec is the third of the observatory’s four instruments to be cleared for regular work..
Live updates: NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope mission
Related: How the James Webb Space Telescope works in pictures
“We made it: NIRSpec is ready for science! This is an amazing moment, the result of the hard work of so many JWST and NIRSpec people and teams over more than two decades,” Pierre Ferruit, Webb project scientist with the European Space Agency (ESA) and principal investigator for NIRSpec, said in the statement. “I am eager to see the first scientific results coming from NIRSpec observations. I have no doubt they will be fantastic. Big thanks to all who made this possible across the years — great job!”
NIRSpec is designed to disperse infrared light from the distant universe into spectra, astronomical “rainbows” that measure how much light is present at which wavelengths. The technique helps scientists reveal the physical properties of observed objects, including their temperature, mass and chemical composition. The final mode the team verified for NIRSpec was the multi-object spectroscopy mode, which is a key capability that allows the telescope to capture spectra from hundreds of different cosmic targets at once — including even the faintest of objects.
“In multi-object spectroscopy mode, NIRSpec can individually open and close about 250,000 small shutters, all just the width of a human hair, to view some portions of the sky while blocking others,” NASA officials wrote in the statement. “By controlling this ‘microshutter array,’ Webb can observe multiple specific targets while reducing interference from others.”
The telescope is equipped with four cutting-edge instruments, which operate in 17 science modes between them. This was the first time that the NIRSpec instrument’s multi-object spectroscopy mode was verified for use from space. Only one mode of the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) is left to be verified before the telescope can commence science operations, according to the statement.
Follow Samantha Mathewson @Sam_Ashley13. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.