More information has come to light regarding the hitchhiking mini-rover on China’s Chang’e 6 sample-return mission to the moon’s far side.
The little Chang’e 6 rover is named “Jinchan” and weighs roughly 11 pounds (5 kilograms), according to China ‘N Asia Spaceflight.
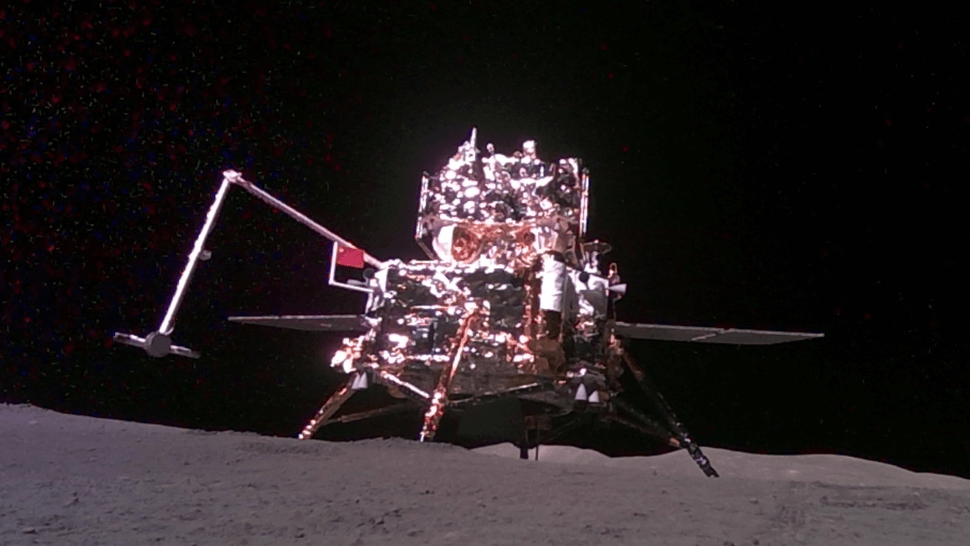
Carried by Chang’e 6 to the far side of the moon, the tiny vehicle rolled into position and snapped an amazing photo of the lander and its outstretched robotic arm that gathered lunar specimens.
The little Chang’e-6 rover is named Jinchan 金蟾 and weighs ~5kg https://t.co/4hCKdM1LwN pic.twitter.com/mcDTtOfwuRJune 29, 2024
Autonomous and intelligent
In a recent story, the state-run Xinhua news agency said that Jinchan was an autonomous, intelligent mini-robot, developed by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
“After Chang’e 6 collected the samples on the far side of the moon,” Xinhua reported, “the mini rover autonomously detached from the lander, moved to a suitable position, selected an ideal angle for the photograph and then captured the image.”
Key materials
In prelaunch imagery of the Chang’e 6 hardware, the four-wheeled mini-rover surprised many China space watchers.
A glimmer of information later came from a story via China’s Science Network, which noted the presence of a Chang’e 6 lunar rover.
According to the article, the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (later referred to as the Shanghai Silicate Institute) undertook the development of a number of key materials.
“The large-sized tellurium dioxide crystal developed by the Shanghai Silicate Institute has excellent acoustic and optical properties and is a key material to achieve a large field of view, high spatial and spectral resolution and is used in the infrared imaging spectrometer of the Chang’e 6 lunar rover,” the story explains.
“The ultrasonic motor is the ‘helper’ that presses the shutter for the ‘Chang’e Family’ lunar rover’s infrared imaging spectrometer. Piezoelectric ceramics are the core material of the ultrasonic motor,” the story continues. “Following Chang’e 3, 4 and 5, the wide temperature range and highly stable piezoelectric excitation element developed by Shanghai Silicate Institute was successfully used in the Chang’e 6 ultrasonic motor.”
X user SegerYU shed further light in a recent post (translation via Google):
“The Chang’e 6 lunar rover has solar panels on the other side, and there are cameras on both sides of the rover, so it can take pictures no matter which side it faces. The rover is fully autonomous and can be remotely controlled from the ground.”
嫦娥六号月球车另一面有太阳能电池板,小月球车两边都有相机,所以小车不管哪边朝着月面都可以拍照。小月球车完全自主控制,地面也可以遥控。另外在最极端的条件下,假如鹊桥二号中继卫星不可用,在完全没有通信的条件下,嫦娥六号有能力自主完成采样、封装等所有月面工作,并自主按时从月面起飞。 pic.twitter.com/K1XMzoAZvGJuly 1, 2024
Clearly different
The sporty mini-rover is far lighter and clearly different than China’s earlier Yutu 1 and Yutu 2 lunar rovers. Each Yutu has six wheels, and both were loaded to their solar panels with lots of equipment.
China’s Chang’e 3 moon lander deployed Yutu 1 in Mare Imbrium after its December 2013 arrival on the moon’s near side.
Yutu 2’s home turf after deployment by the Chang’e 4 lander in January 2019 is Von Kármán crater within the South Pole-Aitken basin, on the moon’s far side. It is reportedly alive and well and still on the move.
You can get more looks at the Chang’e 6 mini-rover here. And check out these good views of the mission’s return capsule after its June 25 landing on Earth, courtesy of China ‘N Asia Spaceflight.