Researchers from the Curtin node of the International Center for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) have made a record-breaking astrophysical discovery while simultaneously uncovering a possible explanation for the rare and extreme astrophysical event known as long-period radio transients.
The study is published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Associate Professor Natasha Hurley-Walker, along with Csanád Horváth, a Curtin University undergraduate student at the time, discovered a pulse of bright energy coming from deep space among archival low-frequency data from the MWA (Murchison Widefield Array), a precursor radio telescope to the SKAO (Square Kilometer Array Observatory). The energy pulse occurs every three hours and lasts 30–60 seconds, making this the longest-period radio transient ever detected.
Long-period radio transients are relatively new to science, and it has been an ongoing mystery how they generate radio waves. With this discovery, researchers believe they have also identified the probable source of the energy burst, potentially shedding light on the long radio transients.
All other previously discovered transients have been deep within our busy galaxy, surrounded by stars, making it challenging to determine precisely what is generating the radio waves.
Associate Professor Hurley-Walker explains, “The long-period transients are very exciting, and for astronomers to understand what they are, we need an optical image. However, when you look toward them, there are so many stars lying in the way that it’s like ‘2001: A Space Odyssey.’ ‘My god, it’s full of stars!’
“In a stroke of good fortune, the newly discovered transient, named GLEAM-X J0704-37, was found on the outskirts of our galaxy, in a much emptier region of space in the Puppis constellation, around 5,000 light years away.
“Our new discovery lies far off the Galactic Plane, so there are only a handful of stars nearby, and we’re now certain one star system, in particular, is generating the radio waves.”
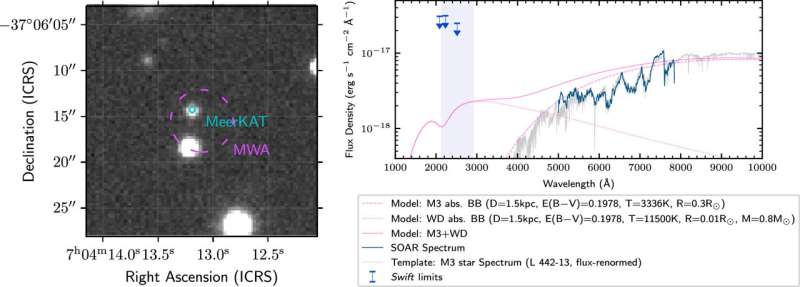
The team was able to pinpoint the location of the radio waves to one specific star using another SKA precursor, the MeerKAT telescope in South Africa. Following up with the SOAR observatory in Chile, they determined the star’s spectrum, finding it was a low-mass star, an “M dwarf.”
This finding both created and answered some pressing questions. Associate Professor Hurley-Walker explains, “An M dwarf alone couldn’t generate the amount of energy we’re seeing.
“The M dwarfs are low-mass stars that have a mere fraction of the sun’s mass and luminosity. They constitute 70% of the stars in the Milky Way, but not one of them is visible to the naked eye.
“Our data suggests that it is in a binary with another object, which is likely to be a white dwarf, the stellar core of a dying star. Together, they power the radio emission.”
The team is working on follow-up observations that will conclusively determine the nature of the system, and the explanation of this extreme astrophysical event.
Discover the latest in science, tech, and space with over 100,000 subscribers who rely on Phys.org for daily insights.
Sign up for our free newsletter and get updates on breakthroughs,
innovations, and research that matter—daily or weekly.
Upon digging through the MWA archives, the astronomers found that GLEAM-X J0704-37 has been active for at least 10 years since the MWA started observing; however, it could have been active and undiscovered for even longer, implying there are still many more to be found in archives around the world.
MWA Director, Professor Steven Tingay, said, “These long-period radio transients are new scientific discoveries and the MWA has fundamentally enabled the discoveries.”
“The MWA has a 55-petabyte archive of observations that provide a decade-long record of our universe. It is like having the data storage equivalent of 55,000 high-end home computers—one of the biggest single collections of science data in the world. It is an absolute gold mine for discovering more phenomena in our universe, and the data are a playground for astronomers,” Professor Tingay said.
More information:
N. Hurley-Walker et al, A 2.9 hr Periodic Radio Transient with an Optical Counterpart, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2024). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad890e
Journal information:
Astrophysical Journal Letters
Astronomers may have discovered the explanation for the longest-period radio transient ever detected (2024, November 26)
retrieved 26 November 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-11-astronomers-explanation-longest-period-radio.html
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.